Fiber optic cables have become an essential component in modern telecommunications, providing high-speed data transmission over long distances. When it comes to fiber optic technology, there are two main types of fiber optic cables which are the single-mode cable and multi-mode cable. The question of which cable to use is a probing thought for most system integrators. Understanding the differences between single mode and multi-mode fiber cables is crucial in making the right choice of fiber optic cables for your application.
Let’s first start by understanding about fiber optic cables itself.
Fiber Optic Cables
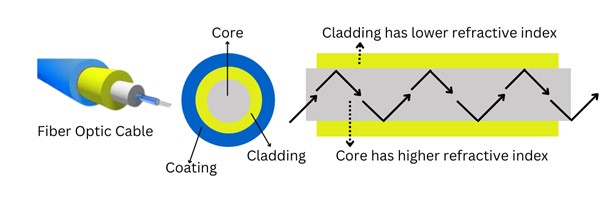
Optical fiber cables transmit optical signals through strands of glass fibers which are placed inside an insulated casing. Fiber optic cables are responsible for the change in data speed consumption and the facelift in the structured cabling industry.
The construction of a fiber optic cable involves five parts, which are the core, cladding, buffer, strengthen member and outer jacket. Core is the central part of the cable made of highest purity glass or plastic through which light travels. Cladding is made up of a material that has low refractive index and surrounds the core. The coating or the buffer surrounds the cladding and is designed to protect the fiber from pinching, shocks, bends et al.
Strengthen member made of Kevlar or gel-filled sleeves provide additional support to the fiber cable by absorbing excessive tension during pulling of the optical fiber. The diameter of the core effects the dispersion of light within the entire length of the cable and gives rise to the single mode and multi-mode type of fiber optic cables. The outer jacket protects the cable from other external damage.
What are the differences between the two types of fiber optic cables: Single-Mode and Multi-Mode
Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable
Single-mode fiber optic cables are designed to transmit a single ray of light through the core of the fiber. The core of a single-mode fiber is very small which is usually 9 micrometers. This narrow core allows for the propagation of a single mode of light, resulting in higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances.
Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Cable:
Multi-mode fiber optic cables, on the other hand, can support the propagation of multiple modes of light simultaneously. The core diameter of a multi-mode fiber is significantly larger, typically ranging from 50 to 100 micrometers. This larger core allows for the transmission of multiple light rays, but it also results in higher signal attenuation and shorter transmission distances compared to single-mode fibers.
Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable Vs Multi Mode Fiber Optic Cable
When to Choose Single-Mode or Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Cable?
The choice between single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic cables depends on the specific requirements of your application and there are other factors like the bandwidth required, transmission distance and installation cost as well your budget for the project that have to be considered.
Let’s look at the key differences in detail between single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic cables:
-
Core Diameter of the Fiber Optic Cable:
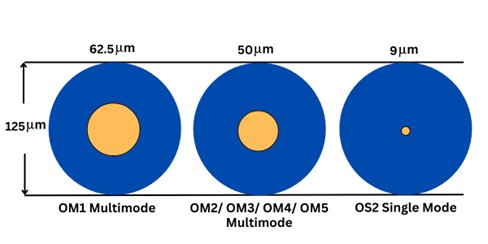
As mentioned earlier the diameter of the core affects the transmission of light rays over the length of the cable. Single-mode fiber has a much smaller core diameter, typically around 9µm. Multi-mode fiber have a larger core diameter and are available in 50 micrometers and 62.5 micrometers.
-
Light Propagation:
Single-mode fiber supports the propagation of a single mode of light. Multi-mode fiber supports the propagation of multiple modes of light simultaneously.
-
Attenuation
Attenuation refers to the reduction in light or signal strength. Multimode fibers generally experience greater attenuation compared to single-mode fibers because they inherently have higher loss at the operating wavelengths of 850 nm and 1300 nm.
-
Transmission Distance
Single-mode fiber can transmit data over longer distances, up to 100 km or more. Due to the larger core size in multi-mode fibers, attenuation increases over longer distances and so its use is limited to shorter transmission distances, typically up to 2 km.
-
Bandwidth
Single-mode fiber has higher bandwidth and lower signal attenuation, allowing for faster data transmission through its small core without interruption. Multi-mode fiber has lower bandwidth and higher signal attenuation, limiting its data transmission speed.
-
Applications:
For long-distance telecommunications, internet backbones, and high-speed data networks, single-mode fiber cables are primarily used. Multi-mode fiber is commonly used in local area networks (LANs), campus networks, and shorter-distance applications.
-
Cost
How expensive the different fiber optic cables are will depend on the volume of cable needed and the other components than make up the system. However, Single-mode fiber optic cables are more cost -effective than the multi-mode FO cables expensive than multi-mode cables. But the multi-mode transceivers are cheaper than the single-mode transceivers.
-
Connector Types
Single-mode fiber typically uses SC or LC connectors. Multi-mode fiber can use a variety of connector types, such as SC, LC.
In summary, the key differences lie in the core diameter, light propagation, transmission distance, bandwidth, applications, cost, and connector types. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the appropriate fiber optic cable for your specific needs.
Single-mode fibers are typically preferred for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, such as telecommunications backbones, internet service providers, and large-scale data centers. Multi-mode fibers, on the other hand, are more suitable for shorter-distance applications, such as building-to-building connections, campus networks, and in-building cabling.
Consulting with a fiber optic expert can help you make an informed decision and ensure the optimal performance of your fiber optic network.